Introduction
Using Liferay’s Objects, we can create custom objects directly through Liferay’s Control Panel, without writing any code. Once created and published, these objects are automatically exposed via REST endpoints using the Headless Object API.
This blog explains how to use headless APIs to perform CRUD (GET, PUT, PATCH, POST, and DELETE) operations on a custom object.
Prerequisites
Liferay DXP/Portal version 7.4+
Basic knowledge of Liferay and REST APIs
Creating a Sample Object
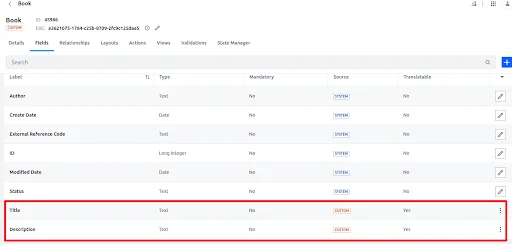
We’ll use a sample custom object called Book, which contains two fields :
Title
Description
Accessing the Headless API
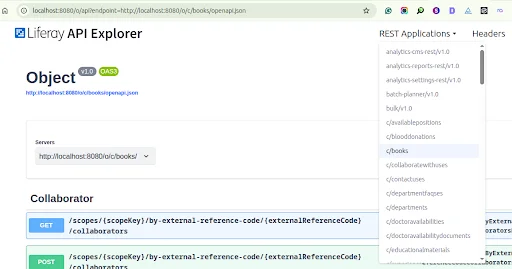
Liferay automatically generates its REST endpoints when a custom object is created and published.
You can view all available APIs at :
- http://localhost:8080/o/api
Look for your custom object (in our case, Book) in the list.
API Endpoints Overview
Once your object is published, Liferay provides the following operations :
- GET – Retrieve object entries
- POST – Create new entries
- PUT – Replace an existing entry
- PATCH – Partially update an existing entry
- DELETE – Remove an entry

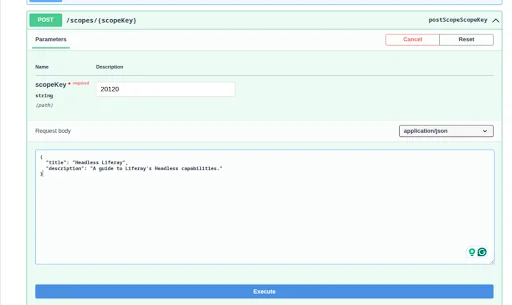
POST – Create a New Book
Use this method to add a new Book entry.
Provide the scopeKey (site ID), and instead of Liferay’s sample payload, provide a payload containing your custom object fields.
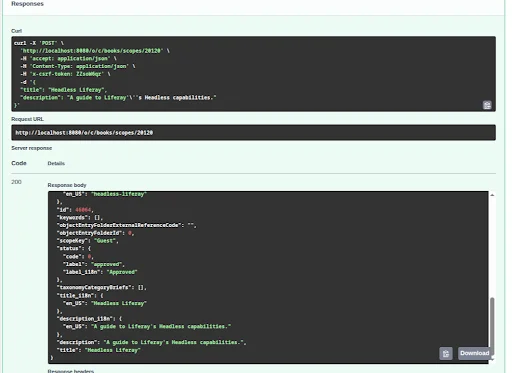
The object entry will be successfully created with a 200 OK response.
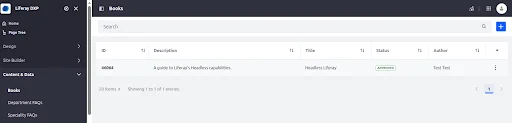
PUT – Replace an Existing Book
Use the PUT method to fully replace an existing Book entry.
Pass the Book entry ID.
Provide a payload with updated values for the fields and execute it.
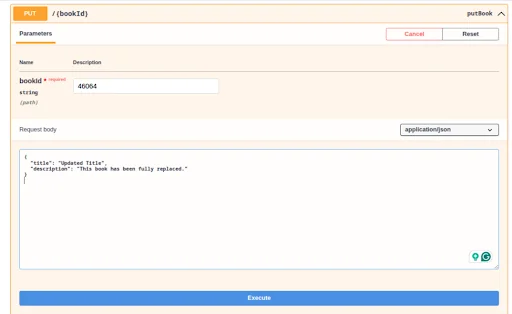
Title and Description will be updated.
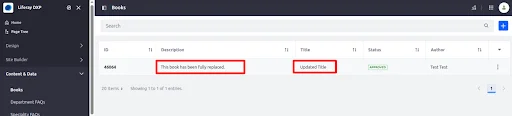
Note : Any fields not included in the payload will be reset or cleared.
For example, if you only pass the title and omit the description, the description will be saved as blank.
PATCH – Partially Update a Book
Use the PATCH method for a specific field change, without affecting other field values,
Pass the Book entry ID.
Provide the payload with the updated values.
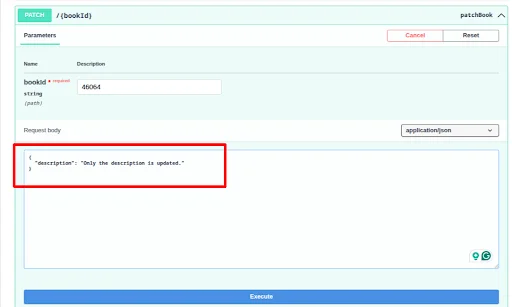
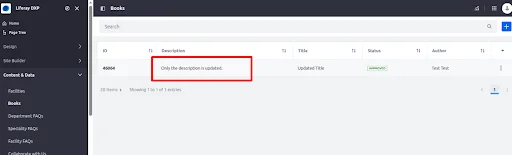
Click Execute, and the entry will be partially updated. All other fields will remain unchanged—for example, only the description will be updated, while the title stays the same.
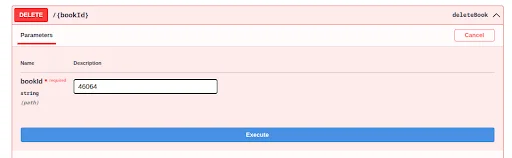
DELETE – Remove a Book
Use the DELETE method to remove a specific Book entry from the list.
Pass the Book ID.
Click Execute, and the entry will be deleted permanently.
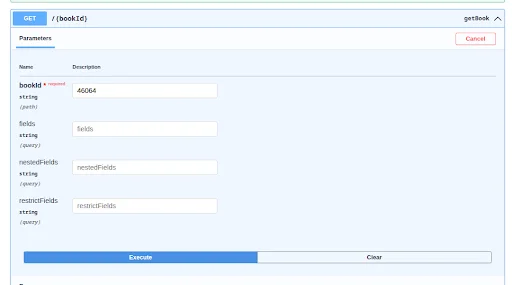
GET – Retrieve Book Entries
Use the GET method to retrieve Book entries.
Pass the Book ID to retrieve a specific entry.
You will receive a full response containing all the fields for the book entry.
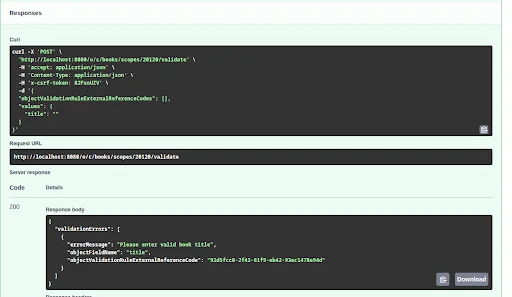
Validate Before Posting
Liferay offers a validation post method endpoint to check if your payload meets the object’s rules before submitting values. This is especially useful for frontend applications to provide real-time feedback.
Example :
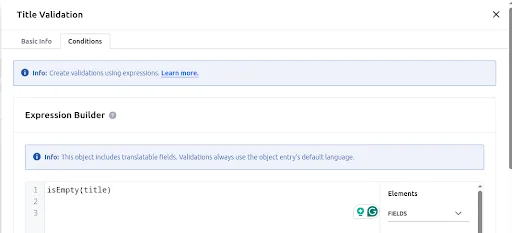
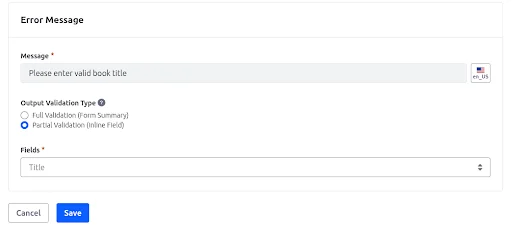
Create a validation in the Book object: If the title field is blank, it will show an error message.
Use the POST method on the validation endpoint.
- Pass the scopeKey (which is the Site ID).
- Provide a sample payload. (with title left blank)
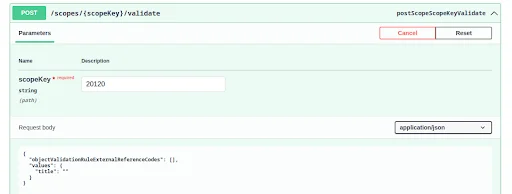
You will receive an error response indicating that the title is required, as per the validation rule defined in the object.
Using External Reference Codes (ERC)
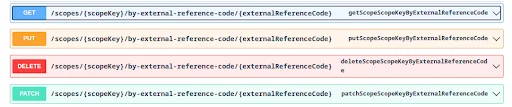
If you’ve assigned an External Reference Code (ERC) to your Book entries, you can also use ERCs in your API requests.
Pass the scopeKey (site ID) and the ERC instead of the object ID.
You can use ERCs with GET, PUT, PATCH, and DELETE operations.
Conclusion
Liferay’s Headless Object APIs are useful for easy-to-manage custom objects. You can build flexible and efficient integrations with minimal effort.